JSP and Servlet in Java
AHMED AMEEN
ROLL NO .04
Client-Server
Architecture
When a client computer sends a data request to the
server through the internet, the server acknowledges the request and provides
the needed digital data to the client.
Client: A client is a person or organization who uses a certain service. A
client is a computer in the digital world that may receive information or use a
specific service from the service providers.
Servers: Similarly, the term “server” refers to a person or medium who serves
something. In the digital world, a server is a distant computer that delivers
data or access to certain services.
Servlet
A Java programme that runs on a Web server
is known as a Servlet. They act as a link between a web browser’s request and
the server’s response.
A servlet’s life cycle consists of three
primary methods.
1.
The init() method
2.
The service() method
3.
The destroy() method
The init() method: There is only one call to the init method. It’s only called once
when the servlet is created, and it’s never called again. It’s used for
one-time initializations.
The service() method: The main method for performing the actual task is the service()
method. To handle requests from browsers and return responses to them, the
servlet container invokes the service() method.
1.
doGet(): This method is called by servlet
service method to handle the GET request from the client.
2.
doPost(): This method is called by
servlet service method to handle the POST request from the client.
The destroy() method: At the end of a servlet’s life cycle, the destroy() function is
only invoked once. This method allows your servlet to conduct cleaning tasks
like closing database connections.
Servlet Life Cycle
For example, two numbers are provided by the client and he wants to perform the addition of that two numbers. Let us see how it works internally.
index.html
It is the interface that is provided to
the client to give two number for addition.
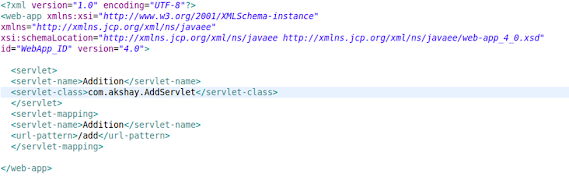
web.xml
As soon as the client clicks on submit
button, it will find which servlet is specified for this request and this will
is done in the web.xml file. After that servlet will be called and the
processing of the request will start.
AddServlet.java
After this client will receive a response
on his/her browser.
JSP
(Java Server Pages)
JSP stands for Java Server Pages, and it’s
a technology for creating dynamic Web pages. This allows developers to embed
java code in HTML pages by using specific JSP tags, the majority of which begin
with <% and end with % >. The only benefit of JSP is that it is simple to
write JSP code for developers.
JSP is internally converted into a servlet.
JSP conversion
Servlets are designed for dynamic web content, after all. However,
there is no effective way to represent dynamic web content on a web page using
Servlets. There are so many that we need to write down out.print() statements.
There can’t be simply one web page in a web application. It’s a collection of
web pages, actually. It is not suggested to create web pages in this manner.
Scriptlet tag: Whatever is written into this tag is converted into a service function in the servlet. The business logic is written into this.
<% java source code %>
Directive tag: This element is used to declare anything that is used by the entire page, such as importing a file.
<%@
directive attribute="value" %>
Declarative tag: This tag is used to declare all variables and statements outside of the service function but within the class.
<%!
field or method declaration %>
Expression tag: Everything inside this tag is printed on the screen.
<%=
statement %>






Comments
Post a Comment